14
2025.1
author
290
Reading volume
OneBasic skill requirements for craftsmen
1. Strong logic, good at analyzing graphics and data;
2. Have basic knowledge of geometry, algebra, calculus, English, etc.;
3. Have professional knowledge of mechanical drawing, mechanical principle, material mechanics, materials science, metrology, etc.;
4. Practical and field experience, as well as the process of continuous accumulation;
5. Basic computer operation, mechanical and process drawing software is better.
TwoFormulation of workpiece process regulations
1. Process analysis of processed parts
(1)Check whether the drawings of the parts are complete and correct;
(2) Review whether the selection of parts and materials is appropriate;
(3) Review the structural workmanship of the parts;
(4) Analyze the technical requirements of the parts.
2. Select the blank
(1)Determine the type of blank:
Blanks: forgings, castings, profiles, welds, etc
(2) Determine the shape of the blank:
Round, square, profiled
3、Determine the machining allowance
(1)Processing allowance:
In order to get a qualified part, the layer of metal that must be cut from the blank
(2) Process allowance:
The difference in the size of the process of two adjacent processes
(3) Total margin:
The sum of the process margins
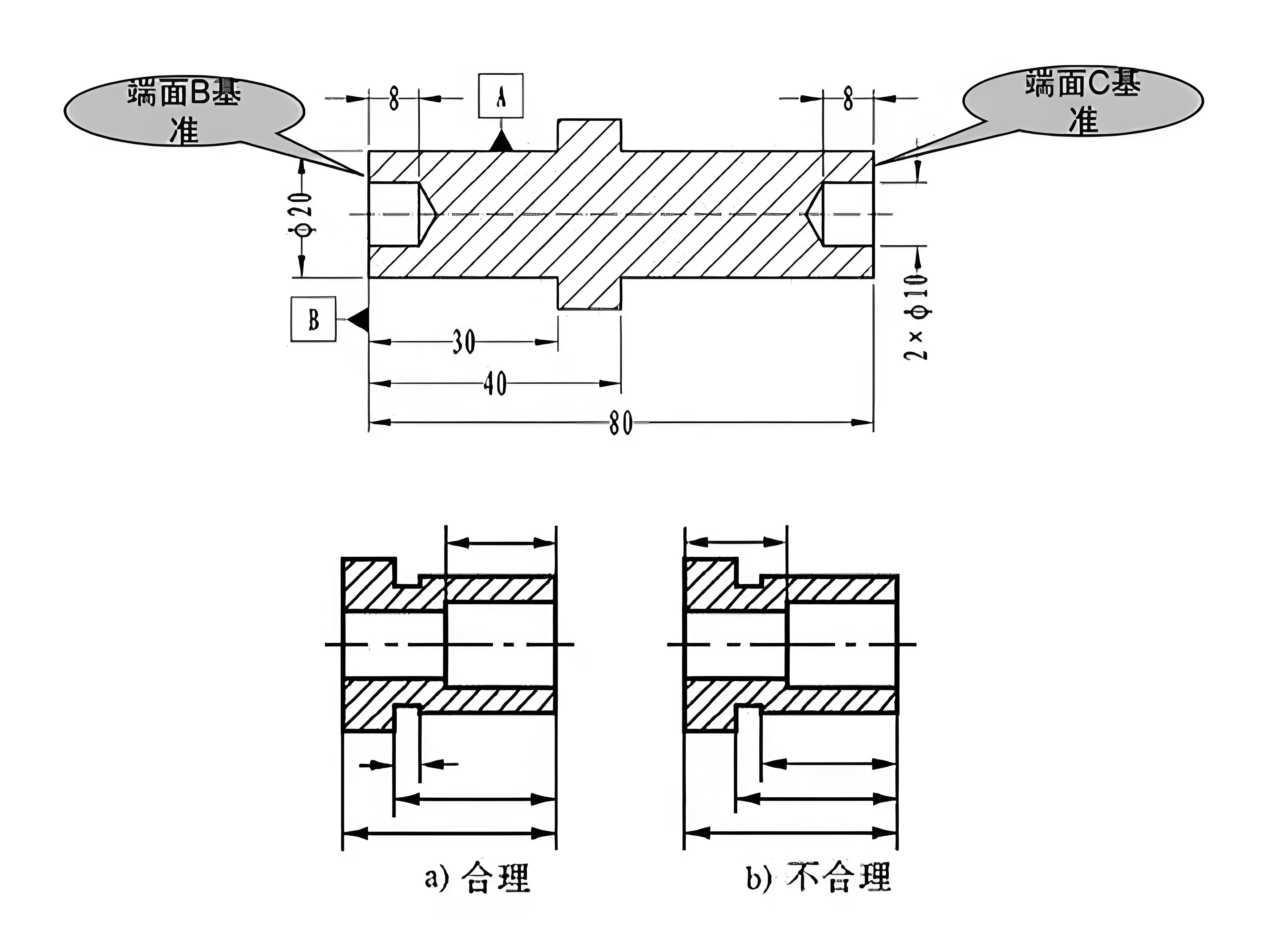
4、Selection of positioning datums
• 基准的概念及分类
(1)Design Benchmarks:
The datum used on the part drawing (on the design drawing).
(2) Process benchmark:
The benchmark on which the process (drawing) is based.
(3) Processing standards:
a. Positioning reference: used as a reference for positioning the workpiece during the machining process.
b. Assembly datum: The datum used to determine the relative position of parts and components in the product during assembly.
(4) Testing benchmark:
The reference based on the dimensions of the surface being processed and the position of the interchange.
5、Formulation of process routes
(1)Determine the processing plan:
• 加工一个直径中25H7表面粗糙度Ra0.8μm的孔。可有四种加工方案:
a. Drilling-reaming-rough twisting-fine twisting;
b. Drilling - rough boring - semi-fine boring - grinding:
c. Drilling - rough boring - semi-fine boring - fine boring:
d. Drilling-rough drawing-fine drawing
According to the characteristics of the processing surface of the part and the output and other conditions, one of the processing schemes should be determined.
(2) Division of processing stages:
a. Roughing stage: Cut off most of the margin on each machined surface and make a fine benchmark.
b. Semi-finishing stage: reduce the error left by rough machining, prepare for the finishing work of the main surface, and complete the processing of some secondary surfaces;
c. Finishing stage: Cut off most of the margin on each machined surface and make a fine benchmark;
d. Finishing stage:Further reduce surface roughness and improve accuracy.
• The purpose of dividing the processing stages is:
① Ensure processing quality;
② early detection of defects in the blank;
③ Reasonable use of equipment;
④ It is convenient to organize production;
(3) Arrangement of processing sequence:
a. Arrangement of cutting and processing processes
① first coarse and then refined;
② benchmark before others;
③ First the main and then second;
④ First face and then hole.
b. Arrangement of heat treatment process
① Preparatory heat treatment: arranged before machining;
② Final heat treatment: arranged after semi-finishing, before grinding processing;
③ Aging heat treatment: arranged after roughing.
c. Arrangement of inspection processes
① Before and after parts are sent from one workshop to another;
② After the end of the roughing stage of the part;
③ before and after the processing of important processes;
④ After all parts are processed;
⑤ First article inspection of important dimensions in process processing.
6、Selection of machine tools and process equipment
(1)Selection of machine tools
a. The accuracy of the machine tool should be suitable for the accuracy required by the process;
b. The productivity of the machine tool should be appropriate to the type of part production;
c. The processing size range of the machine tool should be suitable for the overall dimensions of the parts;
d. It should be in line with the existing actual situation of the factory;
(2)Selection of process equipment
a. Selection of fixtures;
b. Selection of knives;
c. Selection of gages;
7、Preparation of process documents
(1)Machining process card
It is used in single-piece, small-batch production
(2)Used in mass production
It is used in single-piece, small-batch production
(3)Machining technology (comprehensive) card
Used in batch production
ThreeFormulation of workpiece process regulations
1、Direct installation method
The workpiece is mounted directly on the machine tool table or on a universal fixture. Alignment is more time-consuming, and the level of positioning accuracy mainly depends on the accuracy of all tools or instruments, as well as the technical level of the workers.
Therefore, the positioning accuracy is not easy to guarantee, and the production is low, and it is only suitable for small batch production of a single piece
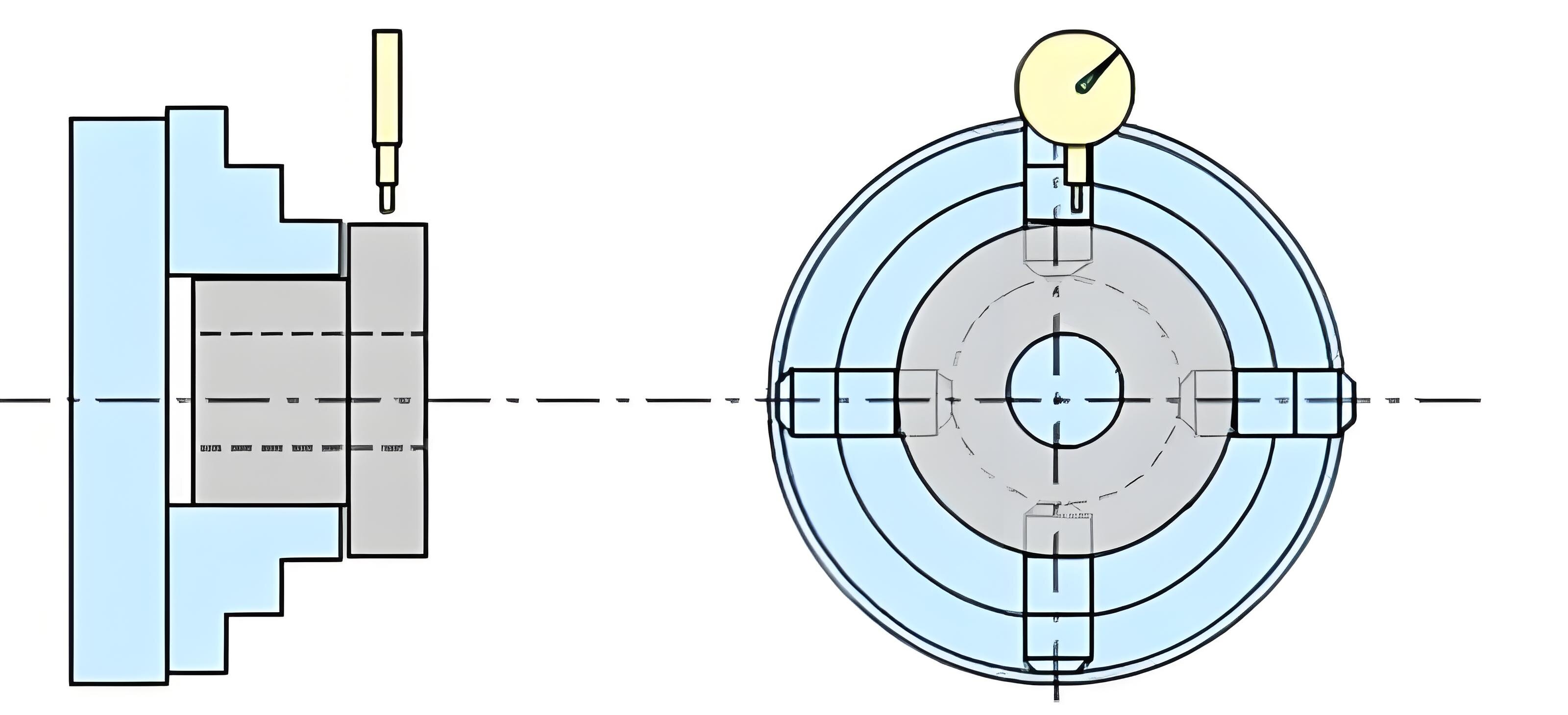
Positioning + Clamping = Mounting
2、The workpiece is mounted on a fixture specially designed and manufactured for its machining
The workpiece is mounted directly on the machine tool table or on a universal fixture. Alignment is more time-consuming, and the level of positioning accuracy mainly depends on the accuracy of all tools or instruments, as well as the technical level of the workers.
So:High positioning accuracy, high production, suitable for mass production
FourTypical part processes
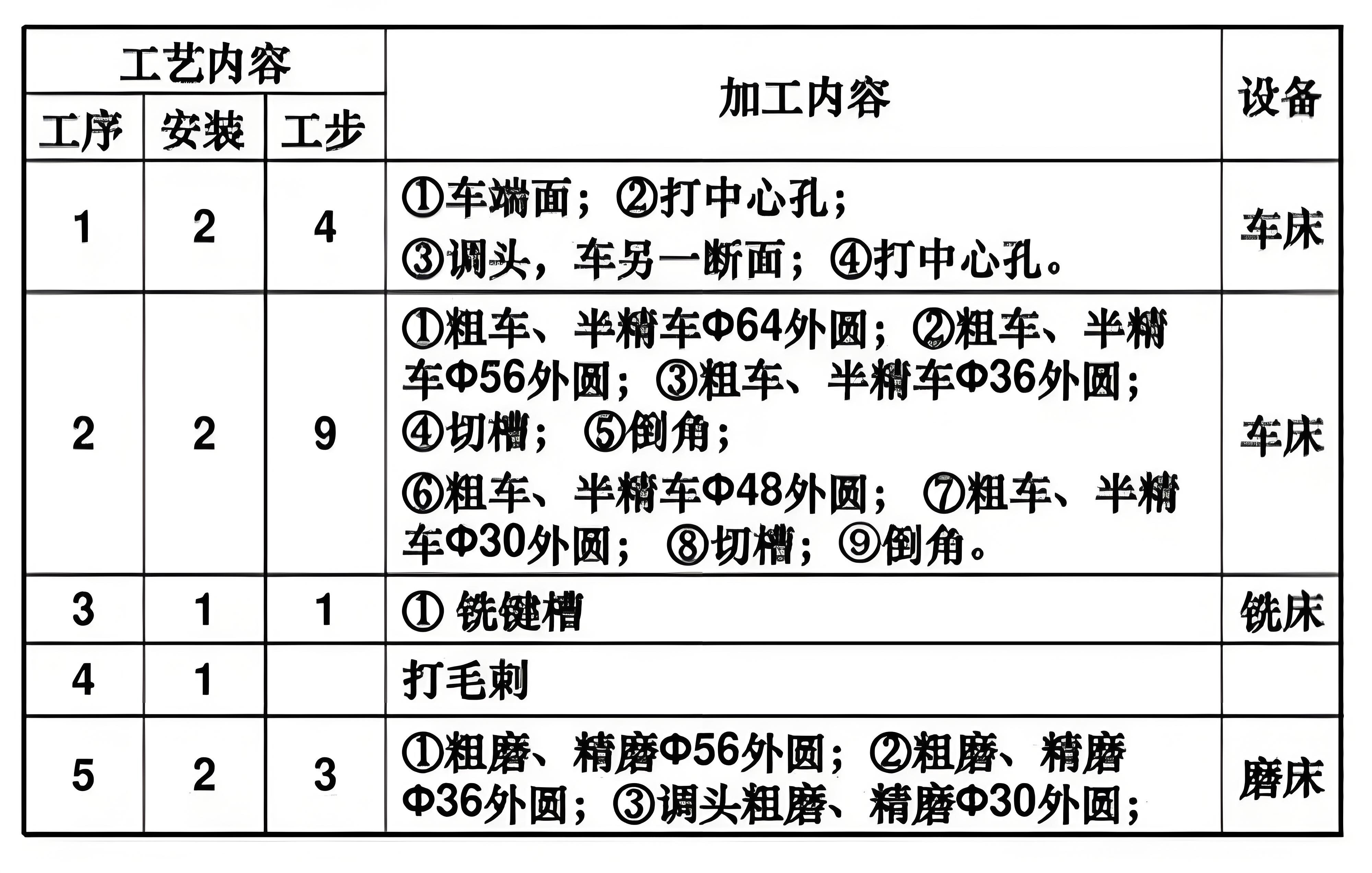
Single-piece, small-batch production
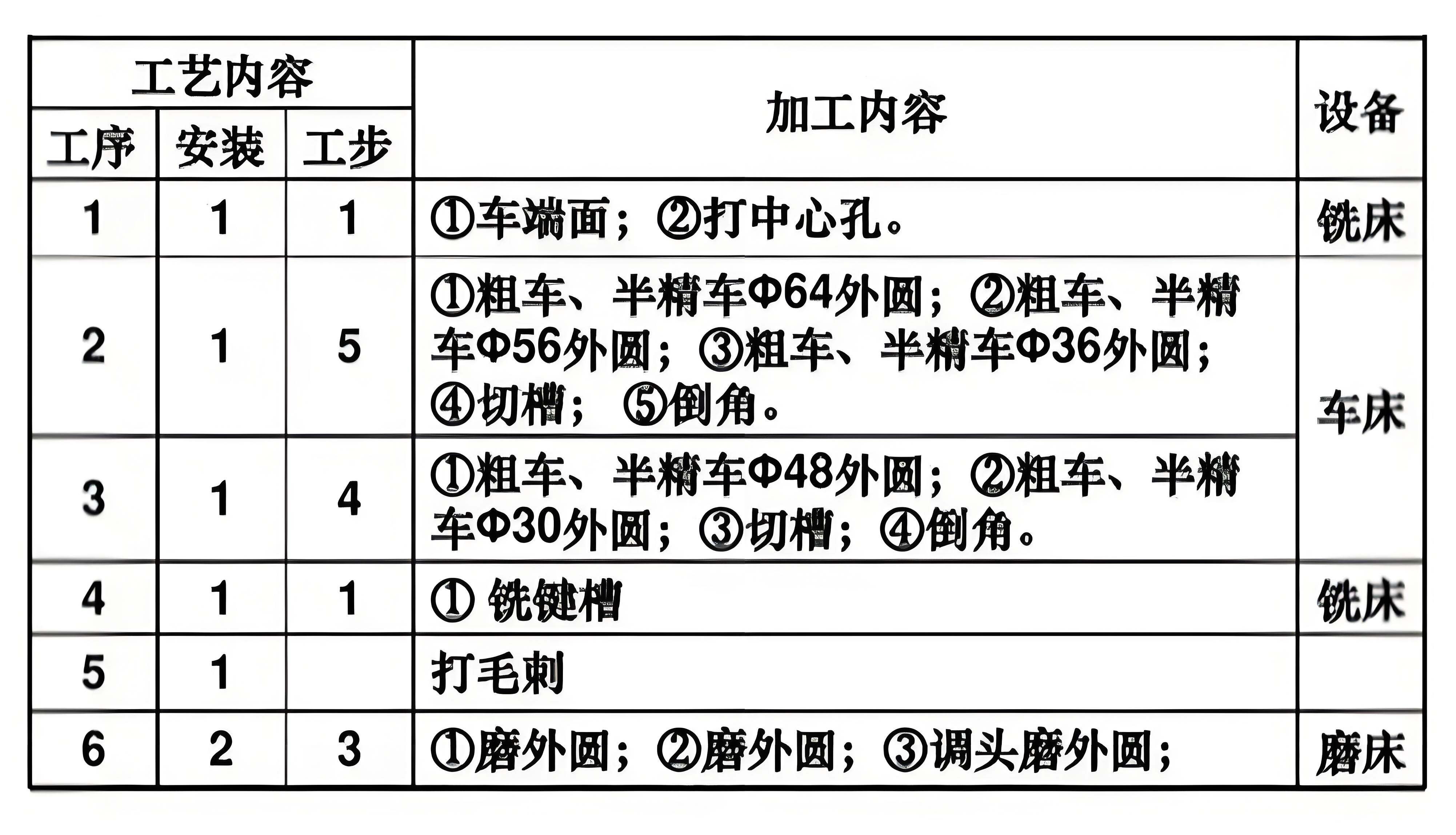
Mass production
