14
2025.1
author
131
Reading volume
OneFixture definition
•jig
When processing a workpiece, a device used to install the workpiece correctly and quickly in order to complete a certain process.
A device used in the mechanical manufacturing process to fix the processing object so that it occupies the correct position for construction or inspection. In a broad sense, any process in the process of installing the workpiece can be called a fixture. For example, welding fixtures, inspection fixtures, assembly fixtures, machine tool fixtures, etc. Among them, machine tool fixtures are the most common, often referred to as fixtures.
The fixture is usually composed of a positioning element, a clamping device, a tool guidance element, an indexing device connection element, and a clamp body (fixture base).
TwoFixture classification
1. General fixture
Standardized fixtures.
As:Machine vises, chucks, indexing heads and rotary tables, etc., have great versatility, can better adapt to the transformation of processing processes and processing objects, their structure has been finalized, the size and specifications have been serialized, most of which have become a standard accessory of machine tools.
Peculiarity:The positioning accuracy is not easy to guarantee, the productivity is low, and it is only suitable for single-piece small batch production.
2. Special fixture
A fixture designed and manufactured specifically for a specific process of a particular part.
Specially designed and manufactured for the clamping needs of a certain product part in a certain process, the service object is single, very targeted, and generally designed by the product manufacturer.
So:High positioning accuracy, high production, suitable for 1,000 mass production.
3、Adjustable clamps
Special fixtures for which elements can be replaced or adjusted.
4、Combination fixtures
Fixtures consisting of standardized components of different shapes, specifications and applications for single-piece, small-batch production and temporary tasks where new product trials and products are frequently changed.
ThreeFixture composition:
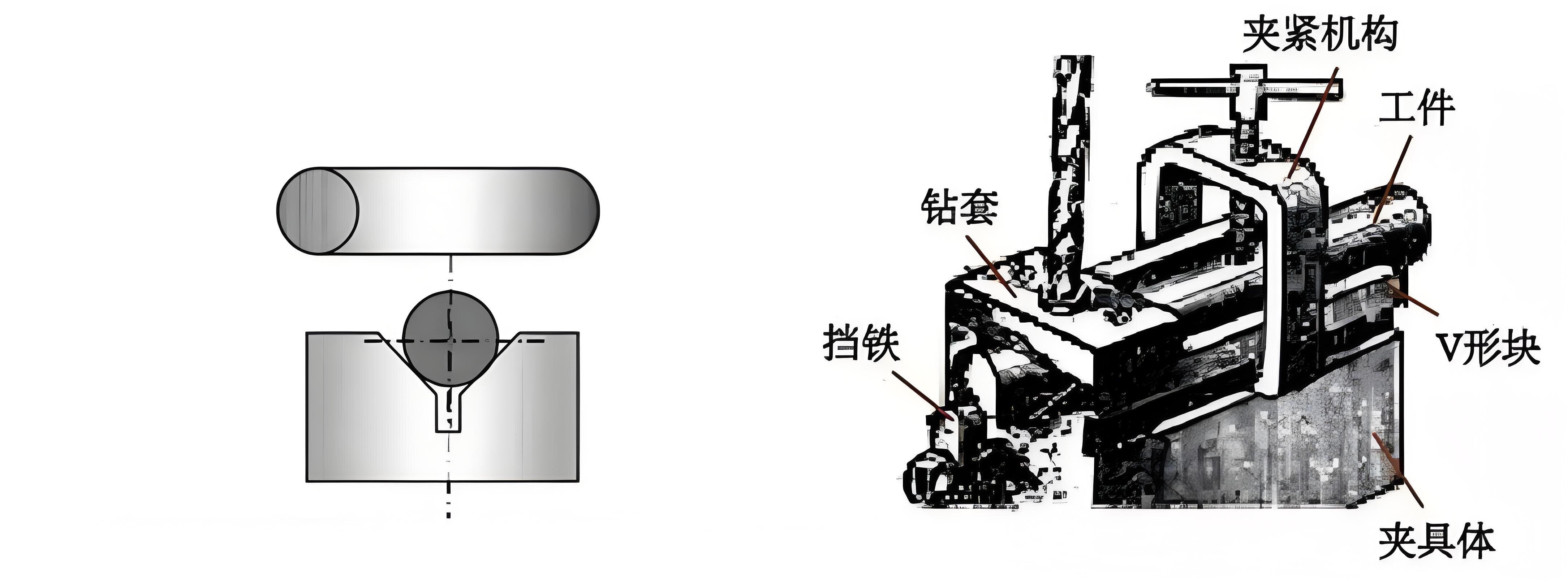
1、Positioning components and devices
Components and devices on the fixture used to determine the correct position of the workpiece.
2、Clamping mechanism and device
After the workpiece is positioned on the fixture, it is clamped to withstand cutting forces, etc.
3、Guide and tool setting elements
Components on the fixture used to align the tool and guide the tool into the correct machining position.
4、Connecting components
The elements on the fixture that determine the correct position of the fixture and the machine.
5、Other components and devices
indexing mechanism, guide key, balance block, etc.
6、Clip the concrete
It is the reference part of the fixture.
FourFixture fixture design and selection guidelines
1. Safety, economy, stability and reliability of workpiece positioning during use;
2. There is sufficient bearing or clamping force to ensure the construction process of the workpiece on the tooling fixture; At the same time, the positioning accuracy of the fixture or workpiece should not be damaged by replacing the clamping point;
3、Meet the simple and fast operation in the clamping process;
4、Wearing parts must be a structure that can be quickly replaced, preferably without the use of other tools to replace them;
5、Meet the reliability of repeated positioning of the fixture during adjustment or replacement;
6. Be able to install in a directional manner and coordinate the positioning surface of the part and the machine tool to maintain a certain coordinate size contact;
7、The clamp should be as open as possible, so a certain safety distance should be maintained between the clamping mechanism elements and the processing surface, and the clamping mechanism elements should be as low as low as low as possible to prevent the clamping mechanism from colliding during the machining process.
8、Avoid complex structures and expensive costs as much as possible;
9、As much as possible, reliable quality standards are selected as constituent parts; give priority to the use of universal and universal combination fixtures;
10、Meet the safety laws and regulations of the country or region where the fixture is used;
11、The design scheme follows the principle of manual, pneumatic, hydraulic and servo in order: special fixtures can be considered for small batch or batch production, and multi-station fixtures and pneumatics can be considered for large production batches; hydraulic clamps;
12、Form the serialization and standardization of the company's internal products.
FiveGage Definition
•Measuring
Measuring instruments that reproduce the measurement value in a certain form.
A measuring tool is the abbreviation of a physical gage, which is an instrument that has a fixed form when used to reproduce or provide one or more known measurement values for quantification. For example, weights, standard batteries, color temperature lamps, resistors, gauges, signal generators, and (Single or multi-valued, with or without a rulerMeasuring instruments are all measuring tools.
The gage generally does not have an indicator, nor does it contain moving parts in the measurement process, but is formed by the measured object itself. For example, the measuring instrument that measures the volume of liquid is to use the upper end face on the liquid as an indicator, and although the adjustable gauge has an indicator device, it is used for the adjustment of the measuring instrument rather than for the measurement of the instrument, such as the measurement in the signal generator.
SixClassification of measuring tools
1、General purpose measuring tool
It is also known as a universal energy tool. It generally refers to the universal measuring tools manufactured by the measuring tool factory. Such as rulers, angle blocks, calipers, etc.
2、Special measuring tools
It may also be called a non-scalar measure. It refers to a measuring tool specially designed and manufactured to detect a certain technical parameter of a workpiece. For example, internal and external groove calipers, wire rope calipers, step gauges and other measuring instruments are measuring instruments that reproduce measurement values in a fixed form.
3、Vernier measuring tool
A gage is a measuring tool used to measure the size, angle, shape accuracy, and mutual position accuracy of parts. Commonly used vernier gauges include: vernier calipers, depth vernier calipers, height vernier calipers, micrometers and dial indicators.
SevenGuidelines for selecting measuring tools
1、Guarantee the accuracy of the measurement
The performance index of the measuring instrument is the main basis for the selection of measuring instrument, and the performance index is mainly the value error, the value variation and the return error.
2、It is selected according to the processing method and quantity
Mass production is mainly based on special measuring tools, gauges and special instruments. A large number of high-efficiency mechanized and automated special measuring instruments are selected.
3、It is selected according to the nature of the part
Measuring instruments are selected according to the structure, characteristics, size, shape, weight, material, rigidity and surface roughness of the part.
4、Select according to the state in which you are located
For example, modern machine manufacturing production automation requires measurement automation. Dynamic measurements are more complex than static measurements.
EightGuidelines for selecting measuring tools
Cutting speed, cutting depth (back cut), and feed (tool passage) are called the three elements of cutting volume.
1、Cutting speed V(m/min)
The circumferential velocity (linear velocity of the main motion) of the surface to be machined on the workpiece is called the cutting speed.
Formula: V = πDn/1000 (m/min)
V: Cutting speed; D: The diameter of the workpiece to be processed (mm); n: Machine tool speed (r/min)
It is usually based on the depth of cutting of the computer machine spindle speed.
2、Depth of Cutting ap(mm)
The vertical distance between the surface to be machined and the surface to be machined is called the depth of cutting.
3、Feed f(mm/r)
When the workpiece rotates for one week, the movement of the turning tool along the feed direction is called the feed volume.
NineCommonly used tool materials
1、Carbon tool steel
Such as T7, T8, T9... T13, etc. It is suitable for making simple hand tools, such as files, saw blades, etc.;
2、Alloy tool steel
Add a small amount of tungsten, chromium, manganese, silicon and other elements to carbon tool steel, which has low heat resistance, such as 9SiCr, etc., and is suitable for making low-speed prototyping tools, such as taps;
3、high-speed steel
It contains more alloying elements such as tungsten, chromium, vanadium, etc., and commonly used are: W18Cr4V, W6Mo5Cr4V, etc. It is suitable for manufacturing medium-speed finishing tools;
4、cemented carbide
The composition consists of WC, TiC and Co and is obtained by sintering method.
Commonly used carbide include:Tungsten, cobalt, titanium (Grade: YTCemented carbide: suitable for processing plastic materials such as steel, its code names are YT5, YT15, YT30, etc., YT5 for roughing and YT30 for finishing;
Tungsten and cobalt (Grade: YGCemented carbide: suitable for processing brittle materials such as cast iron and bronze, its code names are YG3, YG6, YG8, etc., YG8 for rough machining, YG3 for finishing.
